Irrigations can be posted (or entered) in mm, volume, or hours, but the amounts need to be converted to the equivalent depth (mm or ins). Irrigations can also be displayed in depth, volume or hours. However, an area is required to convert between volume and depth.
For example, if 18 litre per vine is applied, what change in mm would be expected in the wetted root zone ?.
If you need a change in the root zone of 25 mm, how many litres should be applied ?

Irrigation amounts posted in volume or hours can be converted using...
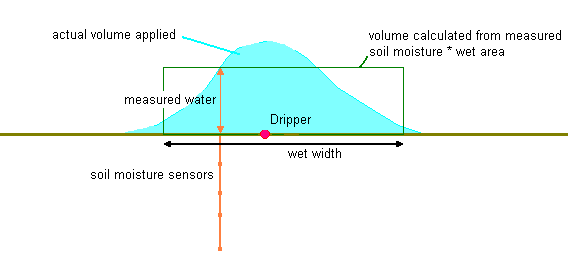
Total Area Method will calculate an amount in mm spread evenly over the entire area. The mm should be less than the mm measured in the soil and the calculated effective amount. With this method efficiencies over 100% are possible.
Wet Area Method will calculate an amount in mm that should be about the same as the change in measured soil moisture. Differences will be due to through-drainage, surface wastage, or poorly positioned sensors.
For example...
VineSpace: 1.8 m |EmitSpace: 0.6 m |RowSpace: 2.4 m |WettedWidth: 1.0m
Emitters: 2 l/hr
6 hours pumping, volume = 6 * 2 * 3 = 18 litres per vine posted...
Total Area Method delivered =18 / (1.8 * 2.4) = 4.2 mm
Wet Area Method delivered = 18 / (1.8 * 1.0) = 10.0 mm
A change in root zone water of approximately 10 mm should be measured, and the software should calculate an effective amount of about 10 mm. Efficiencies will be...
Total Area Method 10 mm / 4.2 mm = 238 %
Wet Area Method 10 mm / 10 mm = 100 %
The calculated delivered amounts (4.2, 10) will be in the ratio...
WetWidth / RowSpace = 1.0 / 2.4 = 0.42 = 4.2/10.0
This ratio will also be the Kc used in the formula...
VolumeRequired = Kc * ETcrop * TotalArea
Probe for Windows will use the Total Area Method if both RowSpace and WetWidth are entered. If they are not entered, or they are the same, the Wet Area Method will be used.
Calculations of required volumes also need an area. Continuing with the example...
| Date | Amount mm | Volume litre/vine | Notes | |
| Water 1 | 10 Dec | 200 | 360 | 360 = 200 * 1.8 * 1.0 |
| Rain | 14 Dec | 5 | 12 | 12=5*1.8*1.0 (assume rain outside wet area not used by crop) |
| Irrigation | 10-17 Dec | 10 | 18 | 10.0mm = 18/(1.8*1.0) |
| Water 2 | 18 Dec | 190 | 370 | 370=190*1.8*1.0 |
| Total used | 10-18 Dec | 25 | 45 | Water1-Water2+Rain+Irrigation |
Therefore, assuming no change in weather, to maintain the soil moisture at 190 mm apply: 45 litres
To bring the soil moisture back to, say, 205 mm apply...
45 + (205 - 190) * 1.8 * 1.0 = 45 + 27 = 72 litres
Drip requirements calculated with...
DepthRequired = DWU * DaysAhead + Correction
VolumeRequired = DepthRequired * WetArea
Scheduling with PDWU
PDWU = (Water1 - Water2 + EffectiveIrrigation + EffectiveRain) / Days
with this example...
PDWU = (200 - 190 + 5 + 10) / 7 = 25/7 = 3.57 mm/day
DepthRequired = 3.57 * 7 + (205 - 190) = 25 + 15 = 40 mm mm
VolumeRequired = 40 * 1.8 * 1.0 = 72 litres
Scheduling with DWU from weather station
A DWU (ETcrop) from a weather station can be used for scheduling, using either 'EstDWU' or 'HistoricalDWU'.
Total Area Method - you need to enter DWU = Kc * ETcrop.
Wet Area Method - you need to enter DWU = ETcrop